6 min to read
逻辑回归原理及其python实现

- content {:toc}
原理
逻辑回归模型:
$h_{\theta}(x)=\frac{1}{1+e^{-{\theta}^{T}x}}$
逻辑回归代价函数:
$J(\theta)=\frac{1}{m}\sum_{i=1}^{m}Cost(h_{\theta}(x^{(i)}),y^{(i)})$
其中:
$$ Cost(h_{\theta}(x),y)= \begin{cases} -log(h_{\theta}(x))& \text{y=1}\ -log(1-h_{\theta}(x))& \text{y=0} \end{cases} $$
该式子合并后:
$Cost(h_{\theta}(x),y)=-ylog(h_{\theta}(x))-(1-y)log(1-h_{\theta}(x))$
即逻辑回归的代价函数:
$J(\theta)=-\frac{1}{m}[\sum_{i=1}^{m}y^{(i)}logh_{\theta}(x^{(i)})+(1-y^{(i)})log(1-h_{\theta}(x^{(i)}))]$
最小化代价函数,使用梯度下降法(gradient descent)。
Want $min_{\theta}J(\theta):$
Repeat {
$\theta_{j}=\theta_{j}-\alpha\frac{\partial}{\partial\theta_{j}}J(\theta)$
} (simultaneously updata all $\theta_{j}$,$\alpha$为学习率)
即:
Repeat {
$\theta_{j}=\theta_{j}-\alpha\sum_{i=1}^{m}(h_{\theta}(x^{(i)})-y^{(i)})x_{j}^{(i)}$
}
正则化(Regularization)
如果我们有非常多的特征,我们通过学习得到的模型可能能够非常好地适应训练集,但是可能不能推广到新的数据集,我们把这种现象成为过拟合。
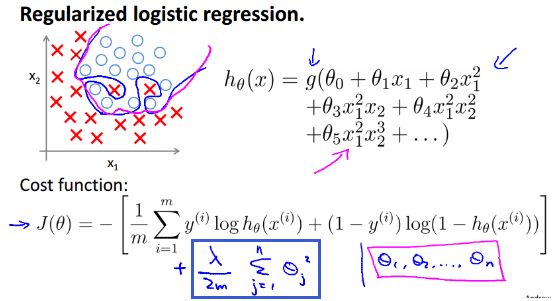
为防止过拟合,提升模型泛化能力,我们需要对所有特征参数(除$\theta_{0}$外)进行惩罚,即保留所有特征,减小参数$\theta$的值,当我们拥有很多不太有用的特征时,正则化会起到很好的作用。
$J(\theta)=-[\frac{1}{m}\sum_{i=1}^{m}(y^{(i)}log(h_{\theta}(x^{(i)}))+(1-y^{(i)})log(1-h_{\theta}(x^{(i)})))]+\frac{\lambda}{2m}\sum_{j=1}^{n}\theta_{j}^{2}$
梯度下降算法:
Repeat until convergence{
$\theta_{0}=\theta_{0}-\alpha\frac{1}{m}\sum_{i=1}^{m}((h_{\theta}(x^{(i)})-y^{(i)})\cdot x_{0}^{(i)})$
$\theta_{j}=\theta_{j}-\alpha\frac{1}{m}\sum_{i=1}^{m}((h_{\theta}(x^{(i)})-y^{(i)})\cdot x_{j}^{(i)}+\frac{\lambda}{m}\theta_{j})$ $for\hspace{1em}j=1,2,...n$
}
python实现
所需数据
代码
# -*- coding:UTF-8 -*-
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
"""
函数说明:梯度上升算法测试函数
求函数f(x) = -x^2 + 4x的极大值
Parameters:
无
Returns:
无
"""
def Gradient_Ascent_test():
def f_prime(x_old): #f(x)的导数
return -2 * x_old + 4
x_old = -1 #初始值,给一个小于x_new的值
x_new = 0 #梯度上升算法初始值,即从(0,0)开始
alpha = 0.01 #步长,也就是学习速率,控制更新的幅度
presision = 0.00000001 #精度,也就是更新阈值
while abs(x_new - x_old) > presision:
x_old = x_new
x_new = x_old + alpha * f_prime(x_old) #上面提到的公式
print(x_new) #打印最终求解的极值近似值
"""
函数说明:加载数据
Parameters:
无
Returns:
dataMat - 数据列表
labelMat - 标签列表
"""
def loadDataSet():
dataMat = [] #创建数据列表
labelMat = [] #创建标签列表
fr = open('testSet.txt') #打开文件
for line in fr.readlines(): #逐行读取
lineArr = line.strip().split() #去回车,放入列表
dataMat.append([1.0, float(lineArr[0]), float(lineArr[1])]) #添加数据
labelMat.append(int(lineArr[2])) #添加标签
fr.close() #关闭文件
return dataMat, labelMat #返回
"""
函数说明:sigmoid函数
Parameters:
inX - 数据
Returns:
sigmoid函数
"""
def sigmoid(inX):
return 1.0 / (1 + np.exp(-inX))
"""
函数说明:梯度上升算法
Parameters:
dataMatIn - 数据集
classLabels - 数据标签
Returns:
weights.getA() - 求得的权重数组(最优参数)
"""
def gradAscent(dataMatIn, classLabels):
dataMatrix = np.mat(dataMatIn) #转换成numpy的mat
labelMat = np.mat(classLabels).transpose() #转换成numpy的mat,并进行转置
m, n = np.shape(dataMatrix) #返回dataMatrix的大小。m为行数,n为列数。
alpha = 0.001 #移动步长,也就是学习速率,控制更新的幅度。
maxCycles = 500 #最大迭代次数
weights = np.ones((n,1))
for k in range(maxCycles):
h = sigmoid(dataMatrix * weights) #梯度上升矢量化公式
error = labelMat - h
weights = weights + alpha * dataMatrix.transpose() * error
return weights.getA() #将矩阵转换为数组,返回权重数组
"""
函数说明:绘制数据集
Parameters:
无
Returns:
无
"""
def plotDataSet():
dataMat, labelMat = loadDataSet() #加载数据集
dataArr = np.array(dataMat) #转换成numpy的array数组
n = np.shape(dataMat)[0] #数据个数
xcord1 = []; ycord1 = [] #正样本
xcord2 = []; ycord2 = [] #负样本
for i in range(n): #根据数据集标签进行分类
if int(labelMat[i]) == 1:
xcord1.append(dataArr[i,1]); ycord1.append(dataArr[i,2]) #1为正样本
else:
xcord2.append(dataArr[i,1]); ycord2.append(dataArr[i,2]) #0为负样本
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111) #添加subplot
ax.scatter(xcord1, ycord1, s = 20, c = 'red', marker = 's',alpha=.5)#绘制正样本
ax.scatter(xcord2, ycord2, s = 20, c = 'green',alpha=.5) #绘制负样本
plt.title('DataSet') #绘制title
plt.xlabel('X1'); plt.ylabel('X2') #绘制label
plt.show() #显示
"""
函数说明:绘制数据集
Parameters:
weights - 权重参数数组
Returns:
无
"""
def plotBestFit(weights):
dataMat, labelMat = loadDataSet() #加载数据集
dataArr = np.array(dataMat) #转换成numpy的array数组
n = np.shape(dataMat)[0] #数据个数
xcord1 = []; ycord1 = [] #正样本
xcord2 = []; ycord2 = [] #负样本
for i in range(n): #根据数据集标签进行分类
if int(labelMat[i]) == 1:
xcord1.append(dataArr[i,1]); ycord1.append(dataArr[i,2]) #1为正样本
else:
xcord2.append(dataArr[i,1]); ycord2.append(dataArr[i,2]) #0为负样本
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111) #添加subplot
ax.scatter(xcord1, ycord1, s = 20, c = 'red', marker = 's',alpha=.5)#绘制正样本
ax.scatter(xcord2, ycord2, s = 20, c = 'green',alpha=.5) #绘制负样本
x = np.arange(-3.0, 3.0, 0.1)
y = (-weights[0] - weights[1] * x) / weights[2]
ax.plot(x, y)
plt.title('BestFit') #绘制title
plt.xlabel('X1'); plt.ylabel('X2') #绘制label
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
dataMat, labelMat = loadDataSet()
weights = gradAscent(dataMat, labelMat)
plotBestFit(weights)
Comments